Binary Lessons
Binary Representation of Characters
In this lesson, students will learn how characters are represented in a computer system.
Learning Objectives:
Curriculum Mapping
Learning Objectives:
- Explain the use of binary codes to represent characters
- Explain the term character set
- Describe with examples (for example ASCII and Unicode) the relationship between the number of bits per character in a character set and the number of characters which can be represented
Curriculum Mapping
KS3 Computing:
- Understand how data of various types (including text) can be represented and manipulated digitally, in the form of binary digits → Students learn how characters are encoded using binary systems like ASCII and Unicode.
- Understand simple Boolean logic and how numbers can be represented in binary → Supports understanding of binary encoding and logical ordering of character sets.
- Use logical reasoning to compare the utility of alternative algorithms for the same problem → Students compare character sets (e.g. ASCII vs Unicode) and their implications.
Data and Computational Thinking:
- Organisation of Data and Data Standards → Students explore how character sets are structured and how bit depth affects representation.
Safe and Responsible Use:
- Legal issues, Legislation concerning ICT → Ethical use of encoded data and implications of character encoding in communication.
- 1.3 Knowledge Constructor → Students evaluate different character encoding schemes and their applications.
- 1.5 Computational Thinker → Students break down character encoding into binary components and model how changes affect representation.
Data and Analysis (DA):
- 2-DA-07: Represent data in multiple ways → Character data is represented as binary codes and compared across encoding schemes.
Algorithms and Programming (AP):
- 1B-AP-15: Test and debug a program or algorithm → Students may write or analyse simple programs that convert characters to binary and vice versa.
- MS-ETS1-1: Define criteria and constraints of a design problem → Students explore constraints in character encoding (e.g. bit limits, language support).
- Science Practices: Analysing and interpreting data → Students analyse how different character sets affect data size and compatibility.
- Crosscutting Concepts: Systems and system models → Character encoding is modelled as a system of binary representations.
- RI.6.8: Evaluate arguments and claims → Students assess the trade-offs between ASCII and Unicode.
- W.8.1: Write arguments with evidence → Students justify encoding choices based on technical and ethical considerations.
- SL.7.1: Engage in collaborative discussions → Group activities around encoding and decoding characters foster discussion and peer learning.
Lesson 1: Theory (Characters)
Suggested time: 50 mins
Starter:
Give students the attached worksheet (Starter.pdf) and ask them to complete the tasks.
Suggested time: 50 mins
Starter:
Give students the attached worksheet (Starter.pdf) and ask them to complete the tasks.
| binary_code_breaker.pdf |
Starter answer sheet
| binary_code_breaker_answers.pdf |
Main:
Explain that, in the previous lesson, the students have looked at how numbers are represented in a computer using binary. Also explain that characters are converted in the same way using something called a character set.
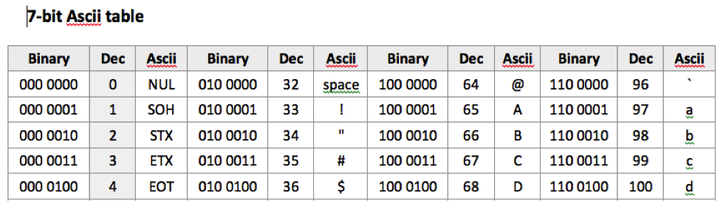
Inform students that one of the most commonly used character sets is ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) and show them the full 7-bit ascii table (See below).
Explain that, in the previous lesson, the students have looked at how numbers are represented in a computer using binary. Also explain that characters are converted in the same way using something called a character set.
Inform students that one of the most commonly used character sets is ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) and show them the full 7-bit ascii table (See below).
| 7-bit_ascii_table.pdf |
Explain that the ascii character set uses 7 bits which allows the computer to encode up to 128 characters.
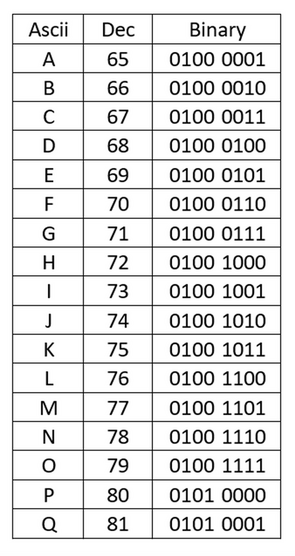
Give students each a worksheet containing part of the ascii table (containing the letters A to Z in uppercase and lowercase) and ask the students to fill in the gaps in the table. Once complete, ask the students to attempt the challenges on the worksheet (see below).
Give students each a worksheet containing part of the ascii table (containing the letters A to Z in uppercase and lowercase) and ask the students to fill in the gaps in the table. Once complete, ask the students to attempt the challenges on the worksheet (see below).
| ascii_secret_agent_challenge.pdf |
Answer sheet:
| ascii_secret_agent_challenge_answers.pdf |
Plenary:
Option 1: Exit ticket
Ask students to complete the following statement:
“Today I learned ______________. One challenge I faced was ______________. Next time, I want to try ______________.”
Option 2: Binary games
Direct students to one of the following binary games:
Option 1: Exit ticket
Ask students to complete the following statement:
“Today I learned ______________. One challenge I faced was ______________. Next time, I want to try ______________.”
Option 2: Binary games
Direct students to one of the following binary games:
Support:
Share the following example if students are struggling with the task.
Share the following example if students are struggling with the task.
Binary to ASCII help sheet
You may be also interested in:
Tags: GCSE, KS4, Theory, Computing Theory, CS Theory, Binary, Binary Representation, binary 2, binary conversion, how to do binary conversion, counting binary, binary number to decimal, binary 101, 8 binary, binary digits, binary digit, meaning of binary